Hematuria, or blood in the urine, can be either gross (visible) or microscopic (blood cells only visible through a microscope). Gross hematuria can vary widely in appearance, from light pink to deep red with clots. Although the amount of blood in the urine may be different, the types of conditions that can cause the problem are the same, and require the same kind of workup or evaluation.
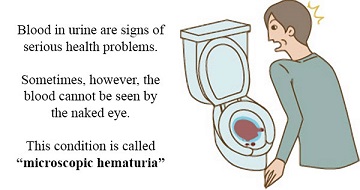
Because blood in urine can be a sign of a serious medical condition, it shouldn't be ignored. All cases of hematuria should be evaluated by a doctor who can order tests to confirm or rule out an underlying cause.
In hematuria, your kidneys — or other parts of your urinary tract — allow blood cells to leak into urine. A number of problems can cause this leakage, including:
Urinary tract infections. Urinary tract infections often occur when bacteria enter your body through the urethra and begin to multiply in your bladder. Symptoms can include a persistent urge to urinate, pain and burning with urination, and extremely strong-smelling urine.
Enlarged prostate. The prostate gland — located just below the bladder and surrounding the top part of the urethra — often begins growing as men approach middle age. When the gland enlarges, it compresses the urethra, partially blocking urine flow.
A bladder or kidney stone. The minerals in concentrated urine sometimes precipitate out, forming crystals on the walls of your kidneys or bladder. Over time, the crystals can become small, hard stones. The stones are generally painless, and you probably won't know you have them unless they cause a blockage or are being passed. Then there's usually no mistaking the symptoms — kidney stones, especially, can cause excruciating pain.
Bladder infections (acute cystitis). In adults, bladder infections usually cause burning or pain with urination. Infants with bladder infections may have fever, be irritable, and feed poorly. Older children may have fever, pain and burning while urinating, urgency, and lower belly pain.
Cancer. Visible urinary bleeding may be a sign of advanced kidney, bladder or prostate cancer.
Inherited disorders. Sickle cell anemia — a hereditary defect of hemoglobin in red blood cells — can be the cause of blood in urine, both visible and microscopic hematuria.
These are possible medical conditions that would lead to blood in urine. Once you see that you have blood in urine, you should go to see your doctor and do some relative tests immediately. Only when you find out the exact cause could you seek for the suitable treatment for it. If your blood in urine is confirmed caused by Urinary tract infections, Bladder infections (acute cystitis), or Enlarged prostate, you could try an effective herbal medicine "Diuretic and Anti-inflammatory Pill". It has strong effects on killing bacterial, eliminating inflammation, clearing the heat and promoting the blood circulation. Thus it could clear up all symptoms of these diseases completely.
 DR.LEE:
DR.LEE: reply
reply
 DR.LEE:
DR.LEE: reply
reply

