An inflammation of the coiled tube (epididymis) at the back of the testicle, which is used to store and carry sperm is called epididymitis. It could occur among men of all ages. Men around the ages of 20 to 39 are most likely to have it.
It is led by bacterial infection in most situations, like gonorrhea or chlamydia and other kinds of STDS.
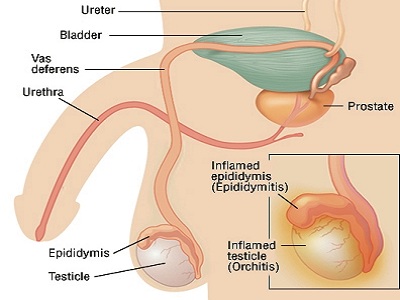
Epididymitis Causes
Usually the cause of epididymitis is bacterial infection. In nearly 80% of the cases, the bacteria accounts for the infection. By moving back through (retrograde), the bacteria always spread from epididymis to the urethra, prostate, vas deferens into the epididymis.
Two common causes of epididymitis in daily life are sexually transmitted organisms and coliforms.
And these two main causes could be divided into below types.
STIs. Sex active young men are more likely to get epididymitis through Gonorrhea and chlamydia.
Other infections. Epididymitis can occur among sex inactive males by a no sexually transmitted bacterial infection. And males are also at high risk of infecting epididymis if they have urinary tract or prostate infections.
Amiodarone. Inflammation of the epididymis can be caused by this heart medication.
Urine in the epididymis (chemical epididymitis). This situation maybe led by heavy lifting or straining and it happens when urine flows backward into the epididymis.
Trauma. Epididymitis can be caused by a groin injury.
Tuberculosis. Rarely, tuberculosis infection can cause epididymitis.
And Other Risk factors include:
Unprotected sex
Structural problems in the urinary tract
Recent urinary tract surgery
Do a urinary catheter
Blockage in the bladder caused by enlarged prostate
Use of the heart medication amiodarone
Being uncircumcised
Heavy lifting or straining
Tuberculosis (TB)
Epididymitis Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of epididymitis might include:
A swollen, red or warm scrotum
Pain and tenderness in the testicles
Pain when urination or an urgent or frequent need to urinate
Discharge from the penis
Pain during intercourse or ejaculation
A lump on the testicle
Enlarged lymph nodes in the groin
Pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen or pelvic area
Blood in the semen
Low-grade fever
Chills
Epididymitis Diagnosis
A physical exam will be done by your physician, which may possibly reveal enlarged lymph nodes in your groin and an enlarged testicle on the impacted side. A rectal examination to check for prostate enlargement or tenderness and order blood and urine tests to check for infection along with other abnormalities perhaps will be done by your doctor.
Other tests your doctor might order incorporate:
Sexually transmitted infection (STI) screening. This includes getting a sample of discharge from your urethra. Your doctor get the sample by inserting a narrow swab in to the finish of the penis, which can be then tested for the presence of bacteria or other infectious organisms. The result is usually employed to choose one of the most efficient antibiotics for treatment.
Ultrasound imaging. This noninvasive test uses high-frequency sound waves to make pictures of structures inside the body and is utilized to rule out situations, which include twisting from the spermatic cord (testicular torsion) or possibly a testicular tumor. If your symptoms began with sudden, extreme discomfort along with other tests haven't been definitive, this test may possibly be used by your doctor.
Nuclear scan with the testicles. Also utilized to rule out testicular torsion, this test requires injecting trace amounts of radioactive material into your bloodstream. Particular cameras then can detect regions inside your testicles that acquire significantly less blood flow, indicating torsion, or extra blood flow, supporting the diagnosis of epididymitis.
Epididymitis Treatment
Therapy includes treating the underlying infection, as well as easing symptoms. Common treatments consist of:
Antibiotics, such as Ceftriaxone, Azithromycin, and Doxycycline for young men, Ciprofloxacin, Ofloxacin, Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim for men who are older than 39.
Pain medication
Anti-inflammatory medication
"Diuretic and Anti-inflammatory Pill" which is a kind of herbal medicine
Rest
Cold therapy (applying cold packs towards the scrotum)
Elevating the scrotum
Wearing an athletic cup for assistance
Abstaining from sexual intercourse
Comprehensive course of antibiotics is really important for you to take to treat the infection. After you have completed the medication to ensure that the infection has been eliminated completely, you must see your physician immediately.
These therapy options are prosperous. On the other hand, you can obtain some instances where much additional invasive therapy is required.
The abscess can be drained by utilizing a needle if an abscess (pocket of pus) has formed.
If no other therapies have been profitable, surgery is absolutely a selection. all or even a part of the epididymis is removed. For any physical defects that could possibly be causing the epididymitis, surgical therapy may well also be necessary to correct.

