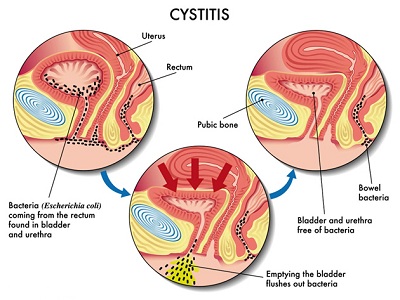
cystitis refers to the inflammation of the bladder. It is caused by a bacterial infection in most of the time. Cystitis usually occurs when the urethra and bladder becomes irritated and inflamed. This condition can be painful and annoying. If left untreated, it can become a serious health problem when the infection spreads to your kidneys. It is more common among females than males.
Cystitis Causes
The causes of cystitis can be various, including the following:
1. When a urinary catheter is changed there may be damage to the area.
2. There is a slight risk of bacteria entering via the urethra when a tampon is inserted in.
3. For those women who use the diaphragm for contraception, the incidence of cystitis may be higher.
4. Frequent and/or vigorous sex can increase the chances of physical damage or bruising, which will aggravate the cystitis condition in turn.
5. Sexually active women have a higher risk of bacteria entering via the urethra.
6. People who don’t empty his/her bladder completely are at higher risk of getting this disease because this can create an environment for bacteria to multiply in the bladder.
7. Women may produce less mucus in the vaginal area during the menopause. This mucus stops the bacteria from multiplying. Menopausal women not on HRT (hormone replacement therapy) have a higher risk of developing cystitis compared to women on HRT.
8. A woman's urethra opening is much nearer the anus than a man's. Consequently, there is a higher risk of bacteria entering the urethra from the anus.
Cystitis Symptoms
Common signs and symptoms of cystitis can be the following:
1. Urine has a strong smell
2. Blood urine
3. Dark and/or cloudy urine
4. Pain in the lower back
5. Pain just above the pubic bone
6. Pain in the abdomen
7. Frequent need to urinate
8.Only small amount of urine is passed each time
9. Burning sensation when urinating
Sometimes, cystitis may be mistakenly regarded as other illnesses or conditions because they may have the same symptoms, such as urethritis, some bacterial infections, prostatitis, chlamydia, gonorrhea, etc.
Cystitis Diagnosis
For cystitis patients, a doctor will ask some questions, carry out an examination, and do an urine test. The urine test will either be sent to a laboratory, or the GP may use a dipstick. A "clean catch" (urine culture) or catheterized urine specimen may be performed to determine the type of bacteria in the urine. Patients who get cystitis regularly may need other further tests such as an ultrasound scan, an X-ray, or a cytoscopy (a fiber optic camera examination) of the bladder.
Cystitis Treatment
1. Antibiotics: Antibiotics are the first line of treatment for cystitis caused by bacteria, while treatment for noninfectious cystitis depends on the underlying cause. The commonly used antibiotics for cystitis include Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, Amoxicillin, Nitrofurantoin, Ciprofloxacin or levofloxacin, and Doxycycline.
2.Herbal Medicines: Herbal medicines are another alternative treatment for cystitis patients. Diuretic and Anti-inflammatory Pill is the most famous one. Unlike antibiotics, it will not cause any side effects and drug resistance. It can help patients with cystitis get cure completely in a short time without recurrence.
3. Painkillers: Painkillers like paracetamol (Tylenol) or ibuprofen can help relieve the discomfort in patients with cystitis. However, you have to discuss this with your doctor before trying this medication as treatment.
4. Cranberry juice: Cranberry juice has been shown to be effective on treating cystitis and other UTIs. Thus, it’s recommended to drink some cranberry juice each day. It can help relieve symptoms and prevent recurrences.

